High-frequency welding
Frequently asked questions about high-frequency (hf) welding
How does high-frequency welding work?
This process uses an electromagnetic field to assemble different layers or parts of thermoplastics. The principle is as follows: an HF voltage heats the various parts subjected to it. The heat emitted causes the different materials to melt under pressure and bond together. After the modified surface has been cooled and held under pressure, the resulting seam is at least as strong as the adjacent surfaces.
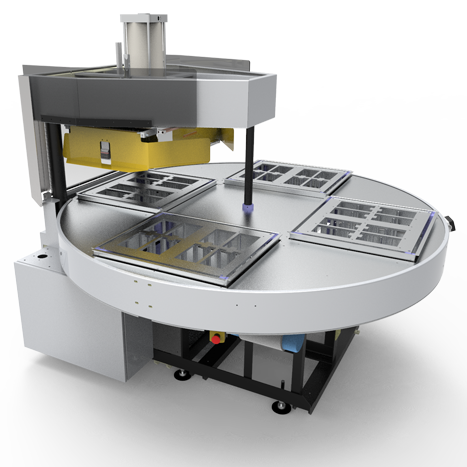
The application is carried out using high-frequency welding machines structured according to the following principle:
- a high-frequency electric field generator, typically 27.12 MHz,
- a pneumatic press for holding the parts to be assembled under pressure,
- electrodes that create a high-frequency electric field, causing the molecules to vibrate and heating the materials,
- a welding bench that holds the parts to be welded in place.
What materials are suitable for high-frequency welding?
While it is technically possible, under certain conditions, to weld metal at high frequencies, the HF welding process is generally used to join plastics. More precisely, it is only used for thermoplastics, the only category of plastics that are deformable when heated. However, even some thermoplastics cannot be welded using this method, such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).
The range of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) derivatives, polyurethane (PU) and polyamides (PA) are the plastics for which high-frequency welding is most widely used. These thermoplastics are used in the manufacture of many everyday objects:
- magazine racks and notebook protectors,
- blisters and plastic packaging,
- tarpaulins and canvas of various sizes
- etc…
What's the difference between ultrasonic and high-frequency welding?
What are the advantages of high-frequency welding?
HF welding is widely used for plastic assemblies because of its undeniable advantages:
- Precision : high-frequency welding is clean and precise, thanks to the possibility of heating only the contact areas of the objects to be joined.
- Made-to-measure: any shape can be used to join 2 parts or 2 components. Some machine models can handle large-format welds (for advertising posters, truck tarpaulins, sails, etc.).
- Joining different types of plastic: fast, powerful heating enables different types of plastic to be combined.
- Speed and rhythm: the HF welding press increases production cycles thanks to its high output rates.
- Joint strength: thanks to the heating mode, the bond is stronger on the inside of the material than “on the outside, with no change after cooling”.
